Clause: যে সব Word বা শব্দ সমষ্টির নিজস্ব Subject এবং Finite Verb থাকা সত্ত্বেও Sentence এর অংশ হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়, তাদেরকে Clause বলে। অর্থাৎ, Clause এমন একটি শব্দসমষ্টি যার একটি Subject ও একটি Finite Verb থাকা সত্ত্বেও বৃহত্তর Sentence এর অংশ হিসেবে কাজ করে। মনে রাখা প্রয়োজন, একটি Sentence যতোটি Finite Verb থাকে ততোটি Clause থাকবে।
Examples:
1. I know What his name is
Clause Clause
নিচের বাক্যটি লক্ষ্য করিঃ
Everybody knows that he confessed his guilty.
বাক্যটির দুটি অংশঃ
(i) Everybody knows
(ii) That he confessed his guilty.
ব্যাখ্যাঃ প্রথমে বাক্যের Subject ও finite Verb যথাক্রমে Everybody এবং Know এবং দ্বিতীয় বাক্যের Subject ও finite Verb যথাক্রমে He এবং Confessed. উভয় অংশে Subject ও Finite verb এর অস্তিত্বের কারণে আমরা প্রত্যেকটি অংশকে Clause হিসেবে অভিহিত করব।
Clause marker: Sentence- এ দুই বা ততোধিক Clause যুক্ত করার জন্য যে সকল Conjunction বা Linker ব্যবহার করা হয় যাকে তাদেরকে Clause marker বলে। যেমনঃ When, While, Before, After, Till, Untill, Since, As, Because, Though, Although, That, So……. that, Sothat, Unless, No Sooner, Where, If, Provided that ইত্যাদি।
Example:
1. The student might come to know if he were present.
clause maker
2. He said that he was ill.
Clause marker
Note: উল্লেখ্য Sentence-এ যতগুলো Clause marker থাকবে তার থেকে একটি বেশি Clause থাকবে।
Clause markers:
(i) Relative Pronoun (who, whom, whose, which, that) conjunction এর মত কাজ করে।
(ii) Relative Adverb (when, why, how, where) Conjunction এর মত কাজ করে।
(iii) Sub-ordinating Conjunction (as, since, because, till, until, though, although, when, as soon as, even if, while, before, after, if, unless, so that, in order that, lest, that)
(iv) Co-ordinating Conjunction (and, but, or, nor. Either ………or, neither……..nor, as well as, not only………but also)
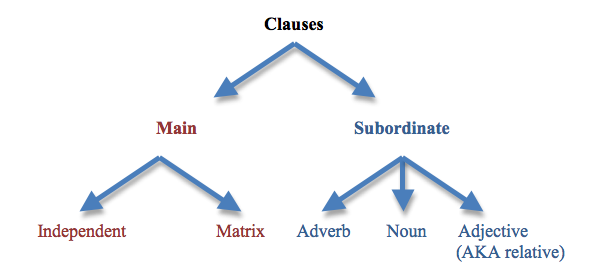
প্রকারভেদঃ
Sentence ও Clause এর ভূমিকা এবং কার্যক্ষমতার উপর ভিত্তি করে Clause কে দুই ভাগ করা যায়।যথাঃ
1. Principal clause/Main clause/Independent clause.
2. Sub-ordinate clause/Dependent clause
Principle clause:
যে সকল clause অর্থ প্রকাশের জন্য কোন clause এর উপর নির্ভরশীল নয় তাদেরকে Principle clause বলে। এই সকল clause গুলো সর্বদা স্বাধীন।
Examples:
Father said that he would come the next day.
The boy came here when he was four.
I that man who helped you.
Note: উপরের Sentence গুলোকে Underline করা অংশটি Principal clause. এই সকল Underlin করা অংশটি কে যদি Sentence থেকে আলাদা করা হয় তবে তারা Simple Sentence হওয়ার যোগ্যতা রাখে।
Sub-ordinat Clause:
যে সকল Clause তার সম্পূর্ণ অর্থ প্রকাশের জন্য Principal clause এর উপর নির্ভশীল এবং Principal clause এর সাহায্য ছাড়া একাকী পূণাংগ অর্থ প্রকাশ করতে পারে না তাদেরকে Sub-ordinat clause বলে।
Example:
1. Father said that he would come the next day.
2. The boy came here when he was four.
3. I know the man who helped you.
Note: উপরে Sentence গুলোতে Underline করা Clause গুলোতে Sub-ordinat clause বলে। এই Sub-ordinat clause গুলো শুরু হয় Clause marker দিয়ে। অর্থাৎ Clause marker এর ঠিক পরের অংশটিই Sub-ordinat clause যা Sentence এর প্রথমে বা শেষে যেখানেই থাকুক না কেন।
Kinds of sub-ordinat clause:
Sub-ordinative clause সমূহ তিন ভাগে বিভক্তঃ
1. Adjective clause
2. Adverbial clause
3. Noun clause
1. The Adjective Clause:
Relative pronoun (who, which, whose, whom) যুক্ত Clause কোন Sentence এ Adjective এর কাজ করলে তাকে Adjective clause বলে। অর্থাৎ, যে Sub-ordinate clause কোন Noun বা pronoun এর পরে বসে Noun/Pronoun/Noun Phrase কে Qualify করে তাকে Adjective clause বলে।
Adjective clause সাধারণত এর কোন Noun/Pronoun কে Qualify করে এবং সব সময় Noun/Pronoun এর পরে বসে। Adjective clause এর পূর্বে সাধারণত Antecedent থাকে।
Examples:
1. The boy, who came here, is my brother.
antecedent adjective clause
2. The machine, which is made in Japan, works well.
antecedent adjective clause
3. This is the man whom Ihelped yesterday.
antecedent adjective clause
এই Clause এ বিভিন্ন Re lative Pronoun গুলো নিম্নক্ত ভাবে ব্যবহৃত হয়ে থাকেঃ
(A) Who/ which/ That =sentence এ Subject হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়ে থাকে।
(i) Who=মানুষের পরিবর্তে বসে
(ii) Which/that=বস্তু /প্রানী/শিশুর পরবর্তে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
Example :
1. I bought a pen Which was red
Principal clause Adjective clause
2. Karim is a student Who reads in class x
Principal clause Adjective clause
3. Nehar is my sister Who sings well
Principal clause Adjective clause
4.I bought a novel that was very interesting.
Principal clause Adjective clause
Note: Adjective clause টিকে Main clause এর মাঝে বসানো যায়। সেক্ষেত্রে Subject এর পর এই Clause টিকে দুটো কমা সহযোগে বসাতে হবে।
Example:
Karim, who works in the factory, is very honest.
Adjective clause
(B) Whom/That=Sentence এ Object হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়ে থাকে।
(i) whom=মানুষের পরিবর্তে বসে
(ii) that=বস্তু/প্রাণী/শিশুর পরিবর্তে বসে
1. I helped an old man whom everybody likes
Principal clause Adjective clause
2. I bought a novel that Shawon borrowed
Principal clause Adjective clause
3. The book, that I bought was very interesting.
Adjective clause
(C) In which/at which/where/for whom/with whom/Preposition+Whom/which=Sentence এ Object of Preposition হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
1. Foyot`s is a restaurant in which/at which/where the French senators eat.
Principal clause Adjective clause
2. Bikash is an orphan boy for whom we have much sympathy.
Principal clause Adjective clause
3. I live in Dhaka where my parents do not live.
Principal clause Adjective clause
(D) Whose+Noun=Sentence এ Subject হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়। Who এর Possessive from হিসেবে whose ব্যবহৃত হয়। (as Possessive form of who)
1. Shima is my friend whose sister is a docter
Principal clause Adjective clause
2. I know Mr. Asfaq whose car is rynning well.
Principal clause Adjective clause
3. Nehal, whose house is newly built, is my friend.
Adjective clause
3. Adverbial Clause:
Adverbial Clause: যে সকল Clause গুলো Sentence-এ ব্যবহৃত হয়ে Adverb এর কাজ করে তাদেরকে Adverbial Clause বলে। এ Clause গুলো Verb, Adjective বা অন্য কোন Adverb কে Qualify করে এবং Principle Clause এর কাজের সময়, স্থান, শর্ত, উদ্দেশ্য, পরিমাণ, ফলাফল, তুলনা, ধরন, কারণ ইত্যাদি প্রকাশ করে।
Examples:
1. Wherever I walked, I found fingerprints. (place)
Adverbial Clause
2. If you work hard, you can pass the examination. (condition)
Adverbial Clause
3. I worked hard so that I could pass the examination. (purpose)
Adverbial Clause
4. The traffic was so heavy that we arrived an hour later. (result)
Adverbial Clause
Kinds: কার্যানুসারে Adverbial Clause কে নিম্নলিখিত ভাগে ভাগ করা যায়।
(A) Adverbial Clause of Time:
(i) যে Clause এ when, while, as, till, until, as soon as , before, after, no sooner, hardly, since ইত্যাদি থাকে এবং এগুলো দ্বারা যে Clause শুরু হয় সেই Clause কে Adverbial clause of time বলে।
(ii) When, as, till, until, as soon as দ্বারা গঠিত Clause এর ক্ষেত্রে একটি Clause এ যে Tense অপর Clause এরও ঠিক একই Tense হবে। While যুক্ত Clause এ Continuous Tense বসে।
(iii) যদি Adverbial Clause of Time টি Main Clause এর সমানে থাকে তবে Main Clause এর পূর্বে কমা বসাতে হয়। আর যদি এই Clause টি Main Clause এর পরে বসে তবে কমা বসাতে হবে না।
Examples:
1. When I was a boy, I visited London.
adverbial clause
2. I saw a big snaks while I was going to Collage.
adverbial clause
3. As he saw the police, he run away in fear
adverbial clause
4. Wait here until I return.
adverbial clause
5. The train heft left the station before we reached there.
adverbial clause
6. IT is many years since my father died.
adverbial clause
7. As soon as he saw the police, he run away in fear
adverbial clause
8. No sooner had he reached the station than the train left.
adverbial clause
(B) Adverbial Clause of Reason :
1. Adverbial clause of Reason দ্বারা Main clause এর ঘটনা কেন ঘটে তার Reason এ বর্ণনা করা হয়ে থাকে । এই Clause কে Reason clause বলা হয় ।
2. এই clause As, since বা Because দ্বারা শুরু হয়। এই clause টি যদি Main Clause এর সামনে বসানো হয় তবে তারপর কমা বসানো হ্য।আর যদি main clause এর পরে বসানো হয় তবে কমা বসানোর প্রয়োজন নেই।
3. সাধারণত Main clause এ যে Tense থাকবে adverbial clause of reason এও ঠিক একই Tense বসবে।
Example: 1. Since I was ill, I did not attend the class.
Adverbial clause
2. I was saved because I had shown a true love for all living things.
Adverbial clause
3. Since the water was salty, the sailors could not drink it.
Adverbial clause
4. As the sets of combs is costly, I can not buy it.
Adverbial clause
(C) Adverbail clause of Concession:
(i) Adverbial clause of concession দ্বারা কোন একটা কিছু স্বীকার করে নেয়া হয়। Though, Although এবং Even if দ্বারা এই clause টি শুরু হয়।
(ii) সাধারণত Main clause এ যে Tense থাকবে Adverbial clause of concession এও একই Tense থাকবে।
(iii) Main clause এর পূর্বে Though/Although/Even if দ্বারা গঠিত Clause কে ব্যবহার করলে কমা ব্যবহার করতে হয়, পরে ব্যবহার করলে কমা লাগে না।
Examples:
1. Though he is poor, he is honest.
Adverbial clause
2. The house looks nice though it is small.
Adverbial clause
3. Although she suffered a lot, she never complained.
Adverbial clause
4. Justice must be done though the heavens fall.
Adverbial clause
(C) Adverbial clause of Concession:
(i) Adverbial clause of concession Though, Although এখন Event if দ্বারা এই clause টি শুরু হয়
(ii) সাধারণত Main Clause এ যে Tense থাকবে Adverbial clause of concession এও একই Tense থাকবে
Main clause এর পুর্বে Though/ Although/ Even if দ্বারা গঠিত clause কে ব্যবহার করলে কমা ব্যবহার করলে কমা লাগে না ।
Examples:
1. Though he is poor, he is honest.
Adverbial clause
2. The house looks nice though it is small.
Adverbial clause
3. Although she suffered a lot, she never complained.
Adverbial clause
4. Justice must be done though the heavenens fall.
Adverbial clause
(D) Adverbial Clause of Result:
(i) Adverbial clause of result এর কাজ হলো Result বা ফল প্রকাশ করা।
(ii) এই Clause টি So……..that বা Such……..that দ্বারা গঠিত।
(iii) So এরপর Adjective অথবা Adverb বসে। কিন্তু such এর পর Noun অথবা Noun-phrase বসতে পারে।
Example:
1. The man was so old that he could not walk.
Adverbial clause
2. I was so ill that I could not attend my classes.
Adverbial clause
3. The river is so difficult that the students can not cross it.
Adverbial clause
4. The sum is so difficult that the students can not solve it.
Adverbial clause
5. The tea was so hot that it burnt my tongue.
Adverbial clause
(E) Adverbial Clause of Purpose:
(i) Main clause এর কাজটি করার পেছনে কোন উদ্দেশ্য রয়েছে Adverbial clause of purpose তা বলে দেয়।
(ii) So that, In order that, Lest দ্বারা এই Clause টি শুরু হয়ে।
(iii) সাধারণত Main clause এ যে Tense থাকে Adverbial clause of purpose এও ঠিক একই Tense ব্যবহার করা হয়।
Examples:
1.Come here so that I may bless you.
Adverbial clause
2.Della went Madame Sofronie so that she could sell he hair.
Adverbial clause
3. The speaker raised raised his voice so that everybody could hear him.
Adverbial clause
4. He walked quietly in order that the child would not wake.
Adverbial clause
Note: যদি So that এবং in order এর পূর্বে that present tense থাকে তবে এদের পরে can/may বসবে এবং সামনে past tense থাকলে পরে could/migh বসবে।
(F) Adverbial Clause of Condition:
(i) Adverbial clause of condition এ একটা শর্ত থাকে এবং Main clause এর কাজটি করার শর্ত কি তা Adverbial clause of condition বলে দেয়।
(ii) এই Clause টি সাধারণত If, Provided that এবং Unless দ্বারা শুরু হয়।
(iii) এই Clause এর অনেকগুলো Type আছে।
Type-1: এই জাতীয় Conditional clause এ ভবিষ্যৎ ঘটনার উল্লেখ করা হয় এবং এতে যে শর্ত থাকে সেটা পূরন হতেও পারে অথবা নাও হতে পারে, কিন্তু শর্ত পুরণের সম্ভাবনা অনেক বেশি।
Structure: If+Present, Future Indefinite/Imperative sentence
Example:
1. If I like it, I shall buy it.
Adverbial clause
2. If it rains, we shall stay at home.
Adverbial clause
3. If you come first, your parent will be delighted.
Adverbial clause
Type-2: এই জাতীয় Adverbial clause of condition এও ভবিষ্যত ঘটনার উল্লেখ করা হয় এবং এতে শর্ত থাকে সেটা অসম্বব না হলে পূরণ হওয়ার সম্ভাবনা কম অথবা বর্তমানে সেটা সত্য নয়।
Structure: If+Past Indefinite, would/could/should+Present form of verb
Examples:
1. If you lived in England, you would speak English fluently.
Adverbial clause
2. If I were you, I would not accept the job.
Adverbial clause
3. If were a bird, I would fly in the blue sky.
Adverbial clause
Type-3: Adverbial clause of condition এ অতীত সত্য ছিল না এমন ঘটনার উল্লেখ থাকে।
Structure: If+ Past Perfect, Would/could/should +Have + Past participle of verb
Examples:
1. If he had worked hard, he would have passed.
Adverbial clause
2. If you had put the bag here, you would have kept an eye on it.
Adverbial clause
3. If he had called me, I would have responded him.
Adverbial clause
Type-4: এই Clause এ will ব্যবহার করা হয়। এটি Request/Polite suggestion প্রকাশ করে।
Structure: If + Future, Future
Examples: 1. If you will study your lesson sincerely, I will give you a nice gift.
Adverbial clause
2.If you will come with me, I will take you there.
Adverbial clause
Type-5: Adverbial clause of condition এ কখনো কখনো If বা অন্য Subordination conjunction ব্যবহার করা হয় না। তখন সাহায্যকারী Verb দ্বারা Conditional clause কে Introduce করা হয়।
Examples:
1. Had I been invited earlier, I would have attended the party.
Adverbial clause
2. Had I the wings of a bird, I would fly away.
Adverbial clause
3. Were I a millionaire, I would introduce free medical facilities for all.]
Adverbial clause
Type-6: কখনো কখনো Relative pronoun, Adjective/Adverb দ্বারা Adverbial clause of condition কে Introduce করা হয়।
Examples:
1. Whatever happens, keep clam.
Adverbial clause
2. Don`t annoy him, whatever you do.
Adverbial clause
3. Whatever may be the result, I shall refuse it.
Adverbial clause
4. Whether you hear from him or hit, you will go must.
Adverbial clause
5. Whether the chief gives him blows or money, he will speak the truth.
Adverbial clause
6. Unless you work hard, you will fail.
Adverbial clause
(G) Adverbial clause of Place:
(i) Main clause এর কাজটি কোথায় সম্পন্ন হয় Adverbial clause of place তা বলে দেয়।
(ii) এই Clause টি সাধারণত where/ Where as ইত্যাদি Sub-ordinating conjunction দ্বারা শুরু হয়।
(iii) সাধারণত Main clause এ Tense যে adverbial clause of place এও ঠিক একই Tense বসবে।
Examples:
1. I have put the book where I can find it.
Adverbial clause
2. The students can stay where they are.
Adverbial clause
3. Mahabub drove his car wherever he wanted to go.
Adverbial clause
4. You will get yourself admitted wherever you like.
Adverbial clause
(H) Adverbial Clause of Degree:
Adverbial clause of degree সাধারণত শুরু হয় As দ্বারা এবং এটি Main clause এ ব্যবহৃত As=Adverb কে Modify করে বা As সম্বন্ধে তথ্য প্রদান করে।
Examples:
1. Kalam is as intelligent as you are.
Adverbial clause
2. I come to college as quickly as I could
Adverbial clause
3. It will happen as sure as death is .
Adverbial clause
4. Nehal is not so quick as you are.
Adverbial clause
3.Noun clasus : Noun clause : যে সকল sub- ordinate clause সাধারণত Noun এর কাজ করে তাদেরকে Noun clause বলে Principal clause এর verb কে what দ্বারা প্রশ্ন করলে উওরে Noun clasue পাওয়া যায় । যেমনঃ
Examples :
1. It is not known when he will arrive.
Noun clause
2. He said that he was ill.
Noune clause
Noune clause subject, complement, case in apposition হিসাবে কাজ করে । এটি সাধারতঃ pronoun (who, What, which, whom, whose), adverb (when, where, why, how,how,long ,how,fat, many, how much) বা Conjunction ( that, whether,if) দ্বারা সুচিত হয় ।
চেনার উপায়;
(i) That/Why ,how, What, When, Which, how long, how many, how much, how fat প্রভৃতি দিয়ে এই Clause শুরু হয় ।
Noun Clause এর প্রকারভেদঃ
1. As the subject of verb: বাক্যের প্রথমে Who,what, that, how, why, when, where, whether Clause Clause Verb Linking verb Subject