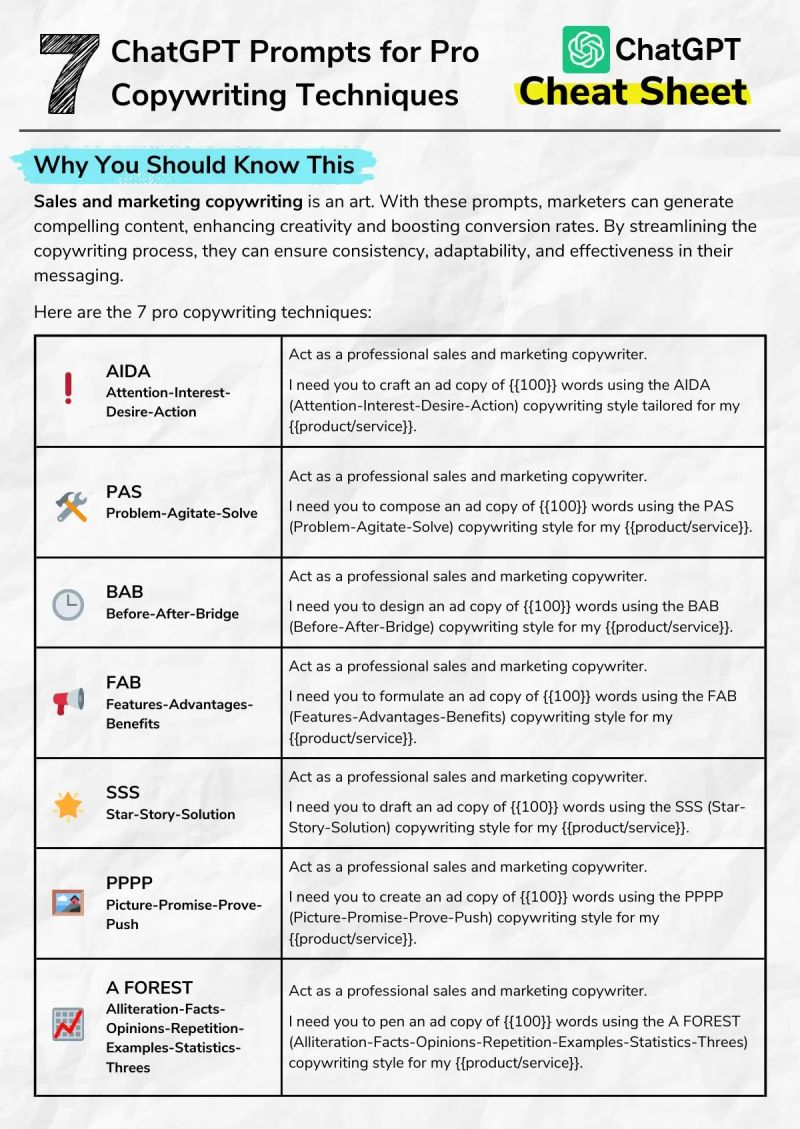
Which AI Tool To Use (And When)
Choosing the right AI isn’t about hype — it’s about fit.
Here’s a quick guide to match the right tool to the right task
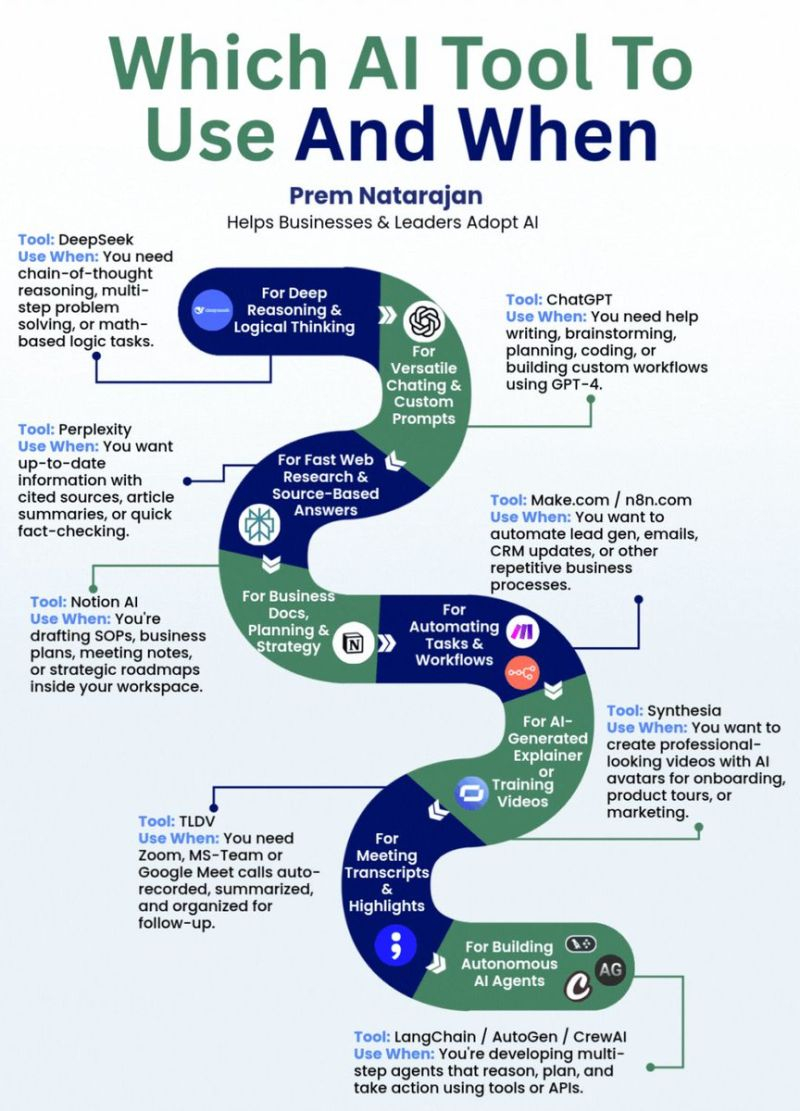
DeepSeek — For Deep Reasoning & Logical Thinking
Use when you need chain-of-thought reasoning, multi-step problem solving, or math-based logic tasks.
ChatGPT — For Versatile Chatting & Custom Prompts
Use when you need help with writing, brainstorming, planning, coding, or building custom workflows using GPT-4.
Perplexity — For Fast Web Research & Source-Based Answers
Use when you need up-to-date info with cited sources, article summaries, or quick fact-checking.
Notion AI — For Business Docs, Planning & Strategy
Use when you’re drafting SOPs, business plans, meeting notes, or strategic roadmaps.
Make(.)com / n8n(.)com — For Automating Tasks & Workflows
Use when you want to automate lead gen, emails, CRM updates, or other repetitive business processes.
Synthesia — For AI-Generated Explainer or Training Videos
Use when you need professional videos with AI avatars for onboarding, product tours, or marketing.
TL;DV — For Meeting Transcripts & Highlights
Use when you need Zoom, MS Teams, or Google Meet calls auto-recorded, summarized, and organized for follow-up.
LangChain / AutoGen / CrewAI — For Building Autonomous AI Agents
Use when developing multi-step agents that reason, plan, and act using tools or APIs.
Choosing the right AI isn’t about hype — it’s about fit.
Here’s a quick guide to match the right tool to the right task
DeepSeek — For Deep Reasoning & Logical Thinking
Use when you need chain-of-thought reasoning, multi-step problem solving, or math-based logic tasks.
ChatGPT — For Versatile Chatting & Custom Prompts
Use when you need help with writing, brainstorming, planning, coding, or building custom workflows using GPT-4.
Perplexity — For Fast Web Research & Source-Based Answers
Use when you need up-to-date info with cited sources, article summaries, or quick fact-checking.
Notion AI — For Business Docs, Planning & Strategy
Use when you’re drafting SOPs, business plans, meeting notes, or strategic roadmaps.
Make(.)com / n8n(.)com — For Automating Tasks & Workflows
Use when you want to automate lead gen, emails, CRM updates, or other repetitive business processes.
Synthesia — For AI-Generated Explainer or Training Videos
Use when you need professional videos with AI avatars for onboarding, product tours, or marketing.
TL;DV — For Meeting Transcripts & Highlights
Use when you need Zoom, MS Teams, or Google Meet calls auto-recorded, summarized, and organized for follow-up.
LangChain / AutoGen / CrewAI — For Building Autonomous AI Agents
Use when developing multi-step agents that reason, plan, and act using tools or APIs.
💡 Which AI Tool To Use (And When)
Choosing the right AI isn’t about hype — it’s about fit.
Here’s a quick guide to match the right tool to the right task 👇
🧠 DeepSeek — For Deep Reasoning & Logical Thinking
Use when you need chain-of-thought reasoning, multi-step problem solving, or math-based logic tasks.
💬 ChatGPT — For Versatile Chatting & Custom Prompts
Use when you need help with writing, brainstorming, planning, coding, or building custom workflows using GPT-4.
🔍 Perplexity — For Fast Web Research & Source-Based Answers
Use when you need up-to-date info with cited sources, article summaries, or quick fact-checking.
📄 Notion AI — For Business Docs, Planning & Strategy
Use when you’re drafting SOPs, business plans, meeting notes, or strategic roadmaps.
⚙️ Make(.)com / n8n(.)com — For Automating Tasks & Workflows
Use when you want to automate lead gen, emails, CRM updates, or other repetitive business processes.
🎥 Synthesia — For AI-Generated Explainer or Training Videos
Use when you need professional videos with AI avatars for onboarding, product tours, or marketing.
📝 TL;DV — For Meeting Transcripts & Highlights
Use when you need Zoom, MS Teams, or Google Meet calls auto-recorded, summarized, and organized for follow-up.
🤖 LangChain / AutoGen / CrewAI — For Building Autonomous AI Agents
Use when developing multi-step agents that reason, plan, and act using tools or APIs.
0 Comments
0 Shares
154 Views
0 Reviews